Installing worn parts
Use of worn valve cotters
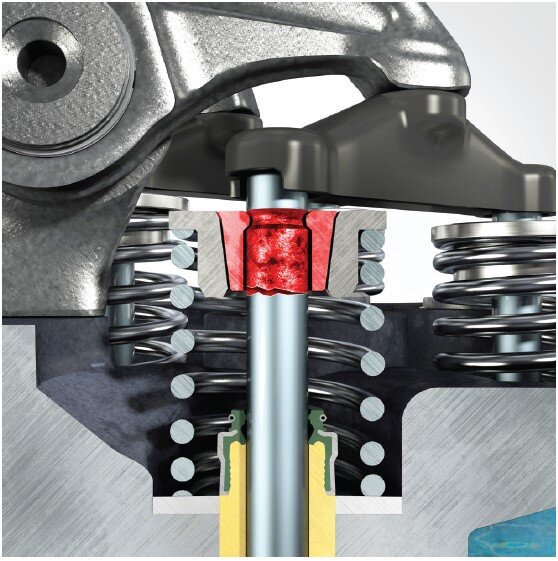
Cause:
Old, worn valve cotters were used during replacement of the valves.
Old, worn valve cotters were used during replacement of the valves.
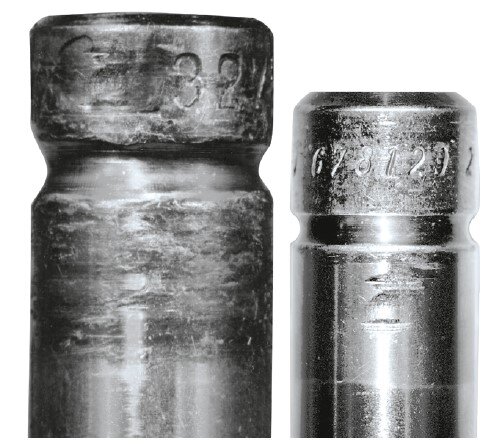

Consequence:
If worn valve cotters are reused, the clamping system can become loose during operation. This results in frictional corrosion on the stem and weakening of the valve in this area. This can cause vibration fatigue failure.
If worn valve cotters are reused, the clamping system can become loose during operation. This results in frictional corrosion on the stem and weakening of the valve in this area. This can cause vibration fatigue failure.
Installing damaged rocker arms/finger type rockers
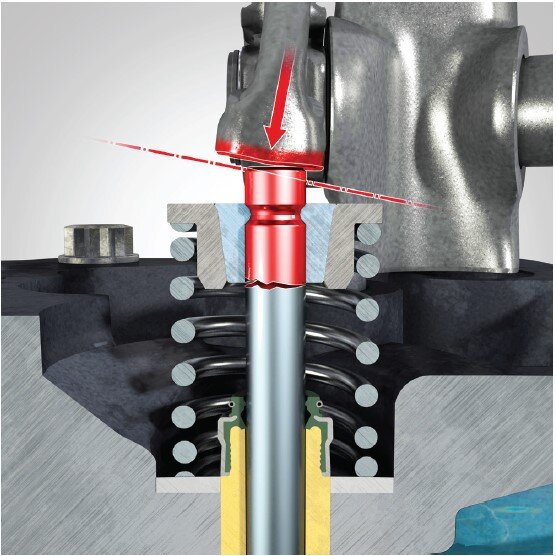
Cause:
Forces are applied eccentrically from the rocker arm to the skirt end face of the valve.
Forces are applied eccentrically from the rocker arm to the skirt end face of the valve.
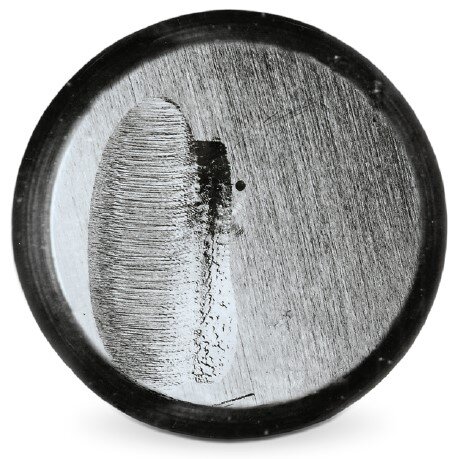

Consequence:
Unilateral wear occurs on the stem and the skirt end. The lateral force on the valve stem caused by the eccentric application of force causes fatigue fractures in the area of the clamping system.
Unilateral wear occurs on the stem and the skirt end. The lateral force on the valve stem caused by the eccentric application of force causes fatigue fractures in the area of the clamping system.
Installing bent valves
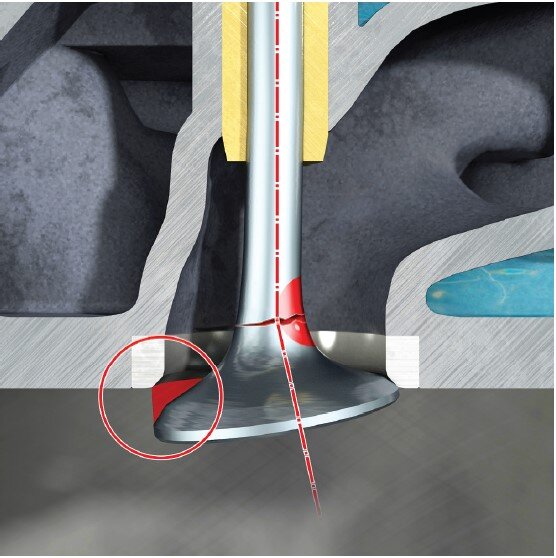
Cause:
A bent valve stem will cause unilateral support of the valve seat on the seating ring.
A bent valve stem will cause unilateral support of the valve seat on the seating ring.

Consequence:
The unilateral stress causes alternating bending stresses and fatigue fractures in the fillet radius at the transition to the stem.
The unilateral stress causes alternating bending stresses and fatigue fractures in the fillet radius at the transition to the stem.