Fractured piston pin
DESCRIPTION OF THE DAMAGE
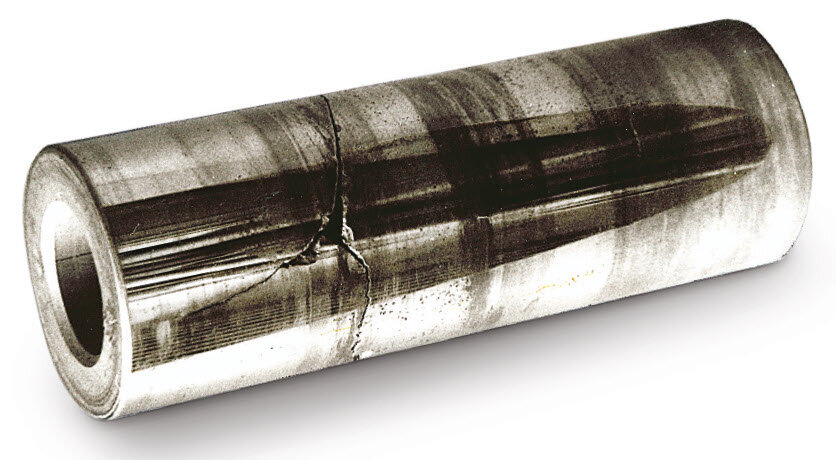
- Lateral fracture on the piston pin (Fig. 1) at the transition between the connecting rod and the piston pin boss.
- Shorter fragment split along its length.
- Fracture surfaces display the characteristics of a fatigue fracture.

DAMAGE ASSESSMENT
Piston pin fractures are caused by excessive loads. Under overstressing conditions, the deformation of the piston pin into an oval shape in the piston pin bores initially causes a longitudinal crack at the ends of the piston pin. This crack can originate both in the exterior surface and on the interior of the bore. The crack then spreads towards the centre of the pin. Inthe area between the piston pin bore and the connecting rod eye that is subjected to the greatest shear stresses and bending stress, the crack then changes direction and becomes a lateral crack. This then ultimately causes the entire piston pin to break right through.
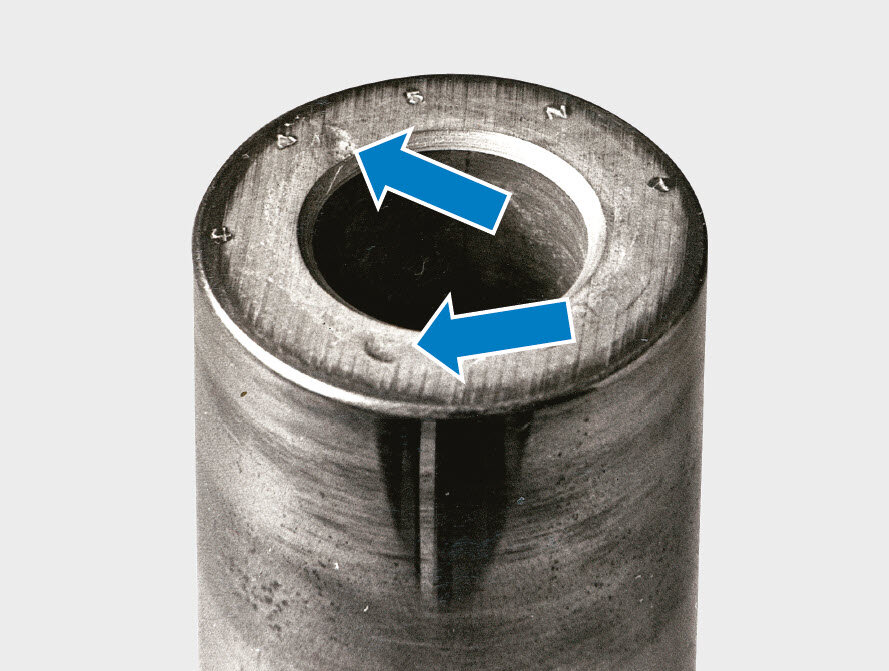
Fig. 2 shows that an incipient crack may not only be caused by overstressing, but also as a result of improper installation of the piston pin. The end face of the broken piston pin clearly shows that the incipient crack was caused by impact damage (hammer blow). An incipient crack can lead to breakage of the piston pin, even under normal load conditions.
Fig. 2 shows that an incipient crack may not only be caused by overstressing, but also as a result of improper installation of the piston pin. The end face of the broken piston pin clearly shows that the incipient crack was caused by impact damage (hammer blow). An incipient crack can lead to breakage of the piston pin, even under normal load conditions.
POSSIBLE CAUSES FOR THE DAMAGE
- Abnormal combustion, often as a result of knocking combustion.
- Hydraulic locks.
- Improper handling of the piston pin during installation.
- Overloading of piston pin through improved engine performance.
- Weakening of piston pin through tuning measures (weight reduction).
- Incorrect piston pin.
Side info