Piston damage and causes
Back to search
Information on diagnostics
Piston seizure or piston broken? What was the cause of the damage? We will help you to correctly diagnose damage in day-to-day repair shop activities and prevent expensive consequential damage.
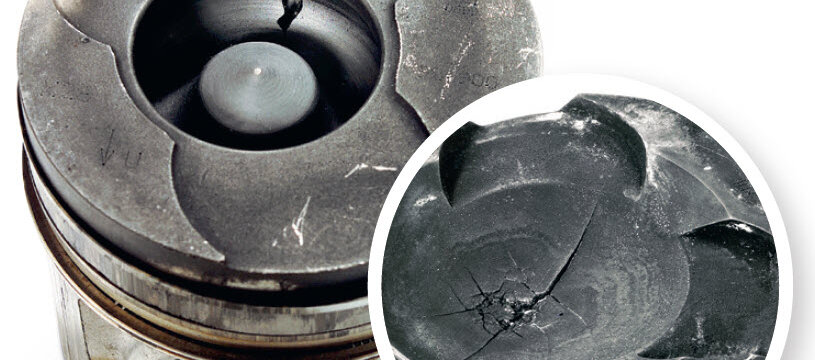
Piston crown damage
Seizure due to overheating (mainly piston crown)
- Overheating due to combustion defaults
- Bent/blocked oil injection jet
- Installation of incorrect pistons
- Malfunctions in the cooling system
- Clearance restriction in the upper sliding surface area
Impact marks
- Piston protrusion too great
- Excessive remachining of the cylinder head sealing surface
- Incorrect valve recess
- Incorrect cylinder head gasket
- Carbon deposits on the piston crown
- Insufficient valve clearance
- Incorrect valve timing caused by incorrect adjustment or a slipped toothed belt
Fused/melted off material
- Faulty injection nozzles
- Incorrect quantity of injected fuel
- Incorrect injection point
- Insufficient compression
- Ignition delay
- Oscillating injection lines
Cracks in the crown and crown bowl
- Faulty or incorrect injection nozzle
- Incorrect injection point
- Incorrect quantity of injected fuel
- Insufficient compression
- Lack of piston cooling
- Installation of pistons with incorrect bowl shape
- Improvement in performance (e.g. chip tuning)
Piston ring damage
Material washout in the ring area
- Incorrectly installed pistons
- Fuel flooding
- Severe axial wear of the ring groove and piston rings
- Ring flutter
Radial wear due to fuel flooding
- Fault during mixture formation
- Combustion defaults
- Insufficient compression pressure
- Incorrect piston protrusion dimension
Axial wear due to ingress of dirt
- Abrasive dirt particles due to inadequate filtration
- Dirt particles that are not completely removed during
reconditioning of the engine (chips, blasting agent) - Abraded particles caused when the engine is being run in
Piston skirt damage
Asymmetrical piston wear pattern
- Bent/twisted connecting rod
- Connecting rod eyes bored at an angle
- Cylinder bore not straight
- Individual cylinders not installed straight
- Excessive connecting rod bearing clearance
45° seizure
- Excessively narrow fit of the piston pin
- Seizure in connecting rod eye (inadequate lubrication at initial start-up)
- Incorrectly installed shrink-fit connecting rod
Dry running/Fuel damage
- Over-rich engine running
- Combustion defaults (misfiring)
- Insufficient compression
- Defective cold-start device
- Oil dilution with fuel
Cylinder liner damage
Cavitation
- Poor/inaccurate seating of the cylinder liner
- Use of incorrect O-ring seals
- Use of unsuitable coolant agent
- Insufficient prepressure in the cooling system
- Operating temperature too low/too high
- Restricted coolant flow
Bright spots in the upper cylinder area
Carbon deposits on the piston top land due to:
- Excessive ingress of oil into the combustion chamber due to defective components
- Increased emissions of blow-by gases with oil entering the intake air system
- Insufficient separation of oil vapour from the blow-by gases
- Frequent idling or short-distance drives