How does an air mass sensor work? (3D animation)
Information on use
How does an air mass sensor work? What mass air flow meter designs are there? What do you need mass air flow meters for? How are mass air flow meters constructed? What do hot-film sensors do in a car? This article gives you the answers.
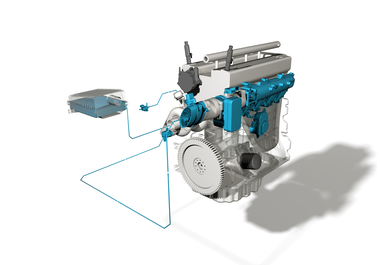
The air mass sensor, also known as the mass air flow meter, is installed between the air filter housing and the intake manifold. Its job is to determine the air mass flowing into the engine and report this data to the engine control. The values are then used to calculate the injected fuel quantity, and, in diesel engines, also for regulating the exhaust gas recirculation. The air mass sensor is, therefore, a key component in the air supply system and for emission control.
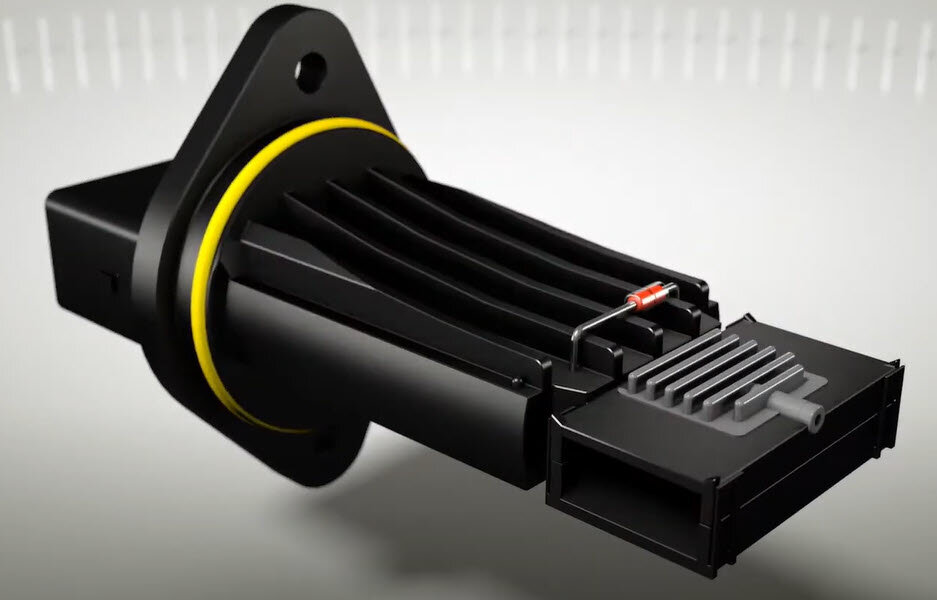
The complete air mass sensor consists of a flow passage (“tube”), in which the intake air flows past the sensor unit itself. Depending on the application and vehicle, the air mass sensor is available as a single plug-in module, or fully integrated in a plastic tube. Both designs are referred to as air mass sensors.
Hot-film sensors
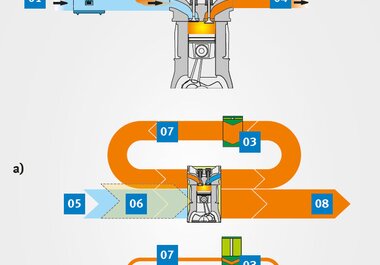
Hot-film sensors are the most modern form of air mass sensors. They contain a sensor plate on which the resistances are applied as a thin film. This enables any changes to be measured quickly and accurately. The sensor is heated up to a constant temperature of around 120 to 180 degrees, depending on the vehicle. The intake air flowing by cools the hot-film sensor. The heating current required to heat the sensor back up to the original temperature can then be used to determine the air mass taken in.