Testing of honing results
Testing options and display of optimum honing parameters
Honing is a fine machining/manufacturing process for almost all materials. It can be used, for example, on piston sliding surfaces for cylinders in combustion engines. The tool used is known as a honing stone, which rotates and moves along the longitudinal axis. The resulting surface can be recognised by the cross-hatch finish. But how do you measure the results of the honing process on a workpiece, and how do you assess the surface or shape? Are there any optimum honing parameters? This article outlines various testing and evaluation options for assessing the surface quality (surface roughness) and roundness deviation in the cylinder.
Assessment options
Roughness tester
Microscope
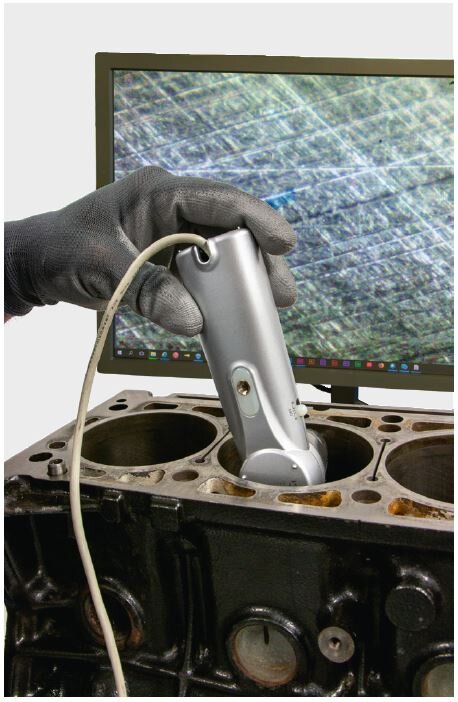

In addition to the roughness record and the measurement report, microscope images are a good method of visualising and documenting the quality of the honing process.
Bore measuring device with dial gauge
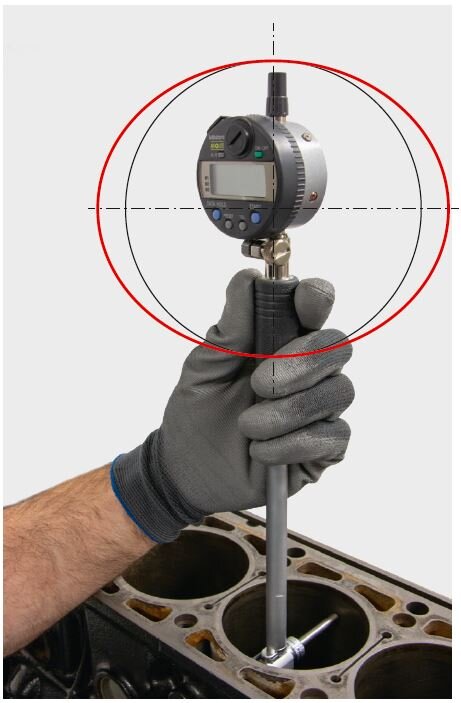

The majority of the cylinder shapes shown below can be determined using the bore measuring device with dial gauge.
Assessment of the surfaces
| Measured value | Description | ||
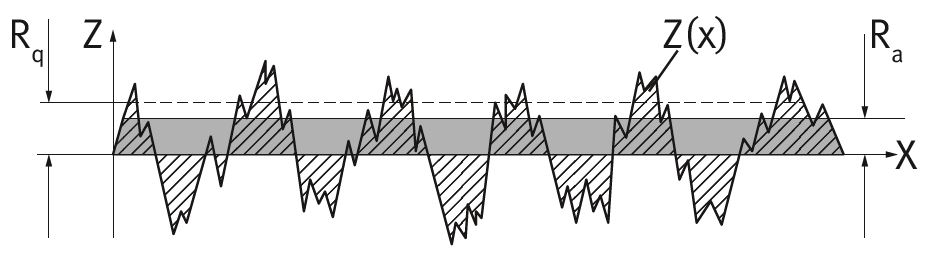
| Mean roughness | Ra | Arithmetic average of all profile values of the roughness profile | 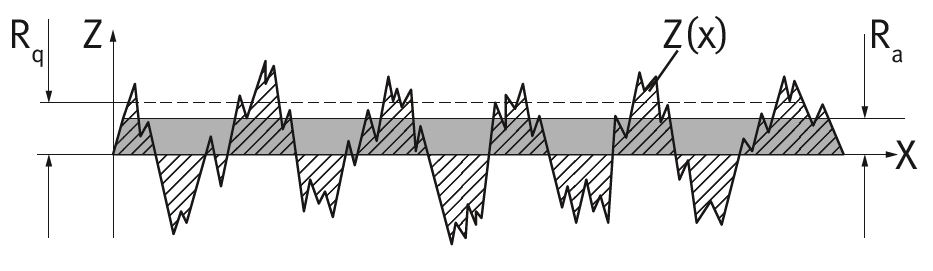 |
| Individual roughness depth |
Rz1 | Sum of the height of the largest profile peak and the depth of the largest profile valley of the roughness profile within a sampling length (lr) |
|
| Roughness depth | Rz | Arithmetic average of the individual roughness depths Rz1 of successive sampling lengths |
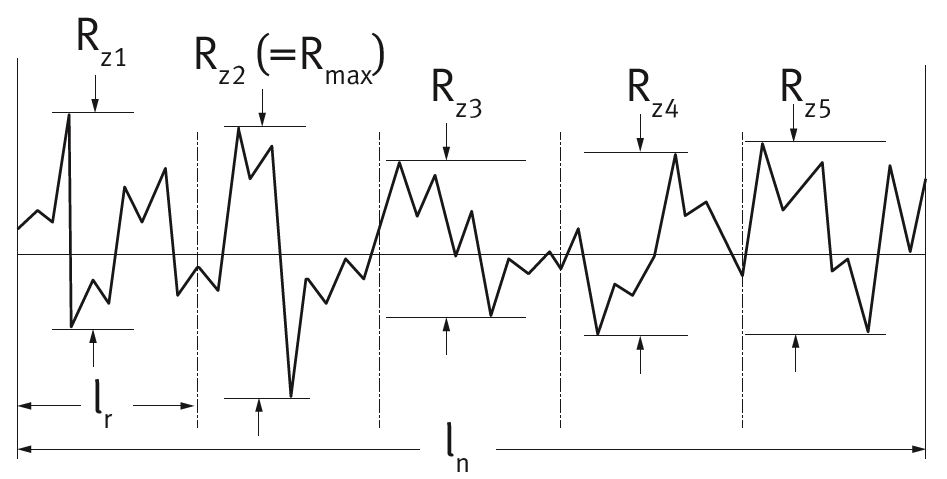 |
| Rmax | Largest individual roughness depth within the entire sampling length |
| Core roughness depth | Rk | Depth of the roughness core profile |
| Reduced peak height | Rpk | Average height of the peaks projecting out of the core area |
| Reduced profile depth | Rvk | Average depth of the valleys projecting out of the core area |
| Material ratio | Mr1 | Smallest material ratio of the roughness core profile |
| Mr2 | Largest material ratio of the roughness core profile |
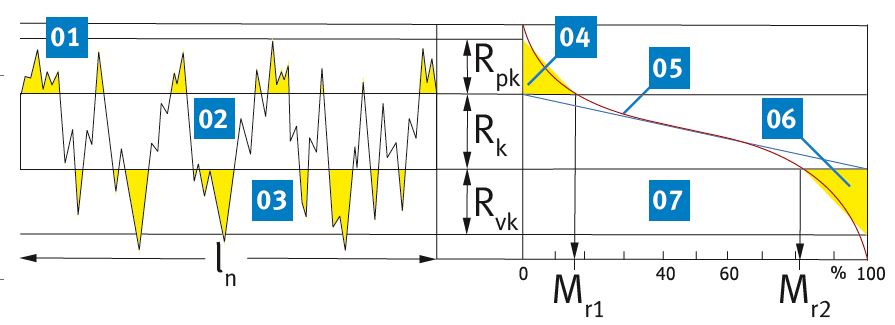
Legend
01 Profile peak surface
02 Core area
03 Profile valley surface
04 “Peak area”
05 Material ratio curve (Abbott-Firestone curve)
06 “Valley surface”
07 Material ratio
| Measured value | Unit | Recommended values Sensing length: 4.8 mm / Sensing tip: 2 μm / 90° |
||
| Petrol / diesel passenger car |
Diesel utility vehicle |
|||
| Arithmetic mean roughness |
Ra | μm | 0.15 to 0.40 | 0.30 to 0.50 |
| Reduced peak height |
Rpk | μm | 0.10 to 0.40 | 0.20 to 0.60 |
| Core roughness depth | Rk | μm | 0.20 to 0.60 | 0.50 to 1.50 |
| Reduced profile depth |
Rvk | μm | 0.50 to 1.00 | 0.50 to 1.50 |
| Smallest material ratio |
Mr1 | % | 4 to 12 | 4 to 10 |
| Largest material ratio |
Mr2 | % | 75 to 90 | 80 to 90 |
| Honing angle | α | ∠° | 25 to 45 | 40 to 60 |
Assessment of shapes and geometries
| Type of fault | Reason for fault | Remedy | ||
 Out-ofroundness Out-ofroundness |
Stage 0: Perfect cylinder |
 |
Correct geometry | |
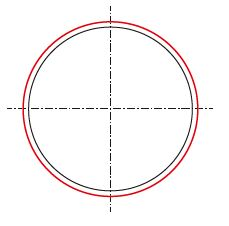
| Stage 1: Eccentricity |
 |
Due to stuck honing head | Check the freedom of movement of the honing head |
|
| Stage 2: Oval cylinder |
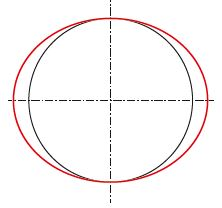 |
Caused by deformation and overheating |
Reduce the cutting pressure – replace the honing stones if necessary |
|
| Stage 3: Triangular out-ofroundness |
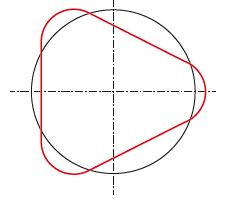 |
Results from distortions from stage 2 and 4 |
For remedies, please see stage 2 and 4 |
|
| Stage 4: Square-shaped faults |
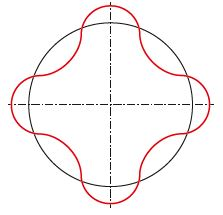 |
Usually caused by distortions resulting from the tightening of the cylinder head bolts |
Reduction in distortion by using a torque plate |
|
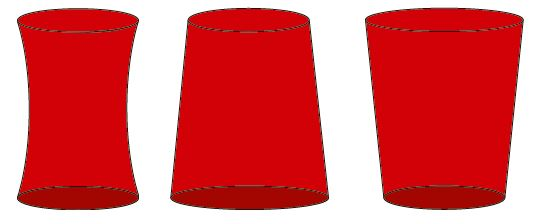 Trumpet, cone and funnel shapes Trumpet, cone and funnel shapes |
Caused by the incorrect stroke position. The stone overrun is too large on the side with the larger diameter |
Correct the stroke position – reduce the stone overrun / use shorter honing stones |
||
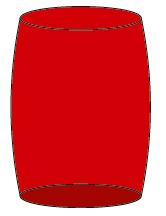 Barrel shapes Barrel shapes |
Caused by honing using too little stone overrun/honing stones that are too short |
Increase stone overrun/use longer honing stones |
||
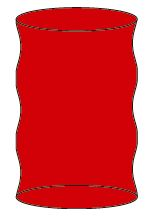 Ripples Ripples |
Caused when extremely short honing stones are used for honing, or when trying to remove narrow points by dwelling on the area with the honing head |
Longer honing stones, short strokes for the targeted processing of narrow points |
Tags
Product groups
This might also interest you
