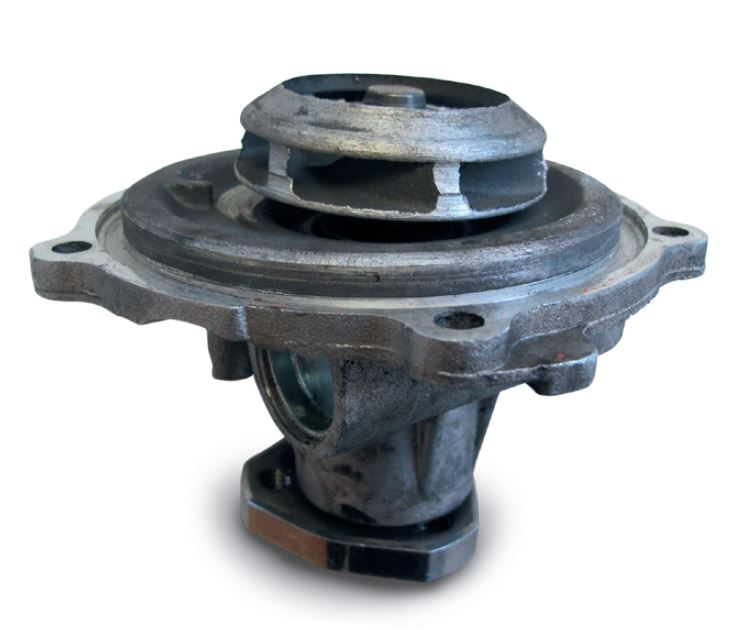

Bearing damage to water pumps
How does water pump damage occur? For example, damage to gaskets can cause coolant agent from the cooling system to penetrate into the bearing housing. Due to the lack of lubrication (lubricant), this can lead to failure and further consequential damage to other components. Timing belts should also be checked for proper alignment on these pumps. You can find more detailed information on these points and other reasons for failure in this article.
Premature bearing damage will always occur if the maximum permissible radial or axial stress is exceeded. If excess cooling liquid is discharged following damage to the sliding ring seal, this can enter into the bearing housing and lead to bearing failure (loss of lubrication, corrosion).

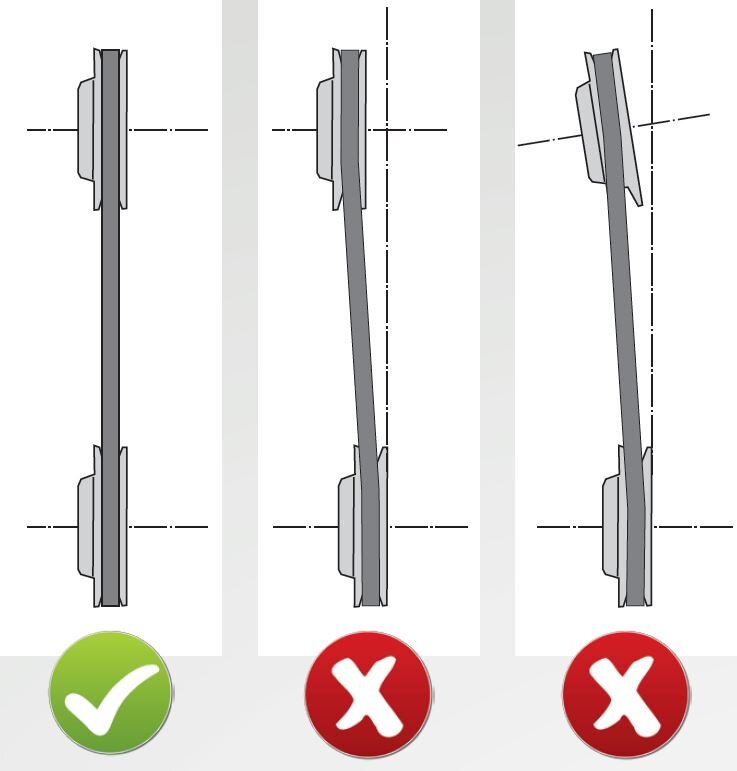


The reasons for failure are:
- Excess tensioning of the drive belt (overstressing of the bearings).
- Insufficient tensioning of the drive belt, leads to increased bearing stress due to the impact of the belt and the torsional vibrations.
- Worn, incorrect or bent pulleys, belt alignment errors, one-sided stress, vibrations (see illustration).
- Automatic tensioners that are defective or incorrectly mounted.
- Defective viscous couplings for the cooling fan (vibrations).
- Fan blades that are defective, bent or incorrect (vibrations).
- Defective vibration dampers on the crankshaft (vibrations, belt alignment errors).
- Incorrect and damaged drive belts.
- Ingress of water into the pump bearing due to:
- Driving through water.
- Cleaning the engine using high-pressure cleaning devices.
- Leaking sliding ring seal (ignoring the loss of coolant from the water pump and constantly refilling the cooling liquid).
- Reaching the end of normal service life due to wear.
- Installing a water pump that is not suitable for the application.
Tags
Product groups
This might also interest you
