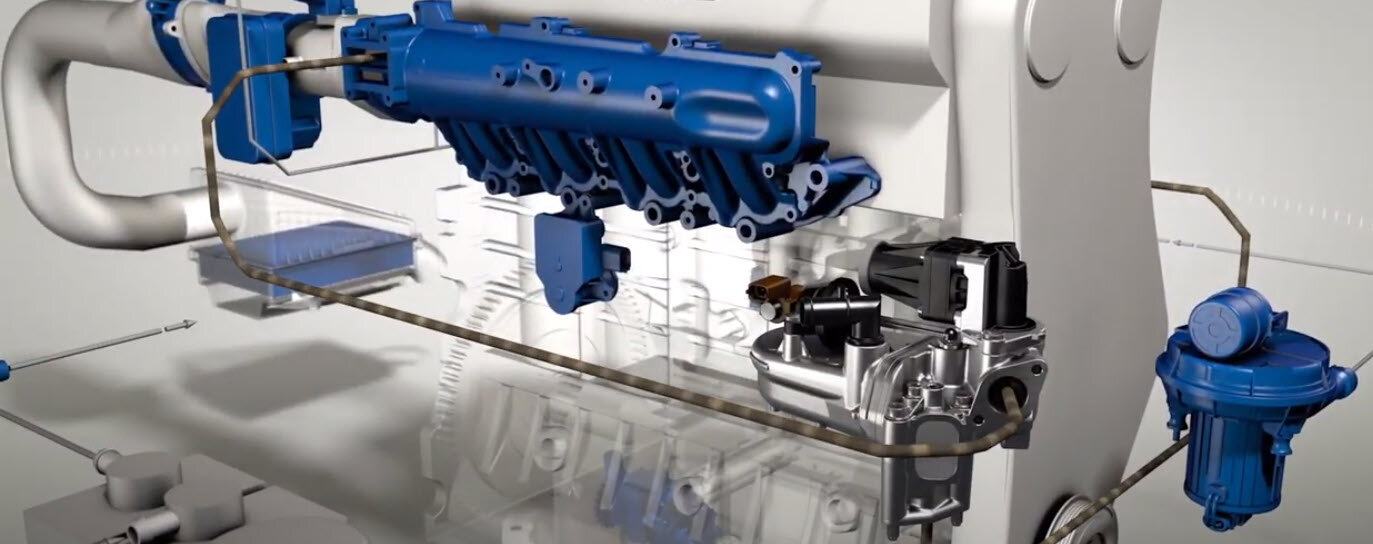
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) made easy
Information on the product
How is cooled exhaust gas recirculation constructed? Why is exhaust gas cooled? How does EGR work? What components does EGR consist of? Why is EGR needed? What do regulating throttles and air mass sensors do? What is “diesel knock”? This article gives you the answers.
0:25 – 1:03
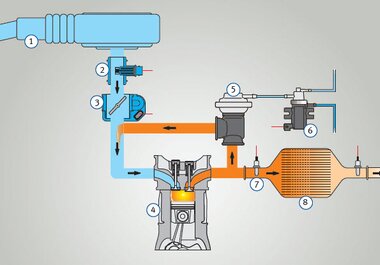
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) reduces harmful emissions from petrol and diesel engines. Exhaust gas is diverted after the cylinders, routed through the EGR valve and mixed back in with the intake air. As a result, less oxygen reaches the cylinders. This leads to a lower combustion temperature, which can reduce the amount of nitrogen oxide by up to 70 percent - as the higher the temperature, the more harmful nitrogen oxides are produced. In petrol engines, this reduces carbon dioxide emissions and fuel consumption.
1:03 – 1:30
The EGR valve is the central component. It determines the quantity of exhaust gas that is recirculated.
There are different designs and models of EGR valves:
- Pneumatic or electrical
- For diesel or petrol engines
- With cooling connections
1:30 – 1:45
Regulating throttles are used in the intake air system in diesel vehicles. They generate the pressure difference required between the exhaust gas and intake side to achieve the necessary high exhaust gas recirculation rates.
1:45 – 2:00
Air mass sensors regulate exhaust gas recirculation in diesel engines. They enable the mass of the recirculated exhaust gas to be calculated.
2:00 – 3:10
EGR coolers are used because the current emissions standards can no longer be met with simple exhaust gas recirculation alone. Cooled exhaust gas reduces the peak combustion temperature even further. This significantly reduces the amount of nitrogen oxides.
Many EGR coolers now feature an electrical or pneumatically operated bypass flap. This allows the exhaust gases to be directed past the EGR cooler in the warm-up phase, to quickly bring the engine and catalytic converter up to operating temperature. This reduces the amount of noise, known as “diesel knock”, as well as the level of raw hydrocarbon emissions.